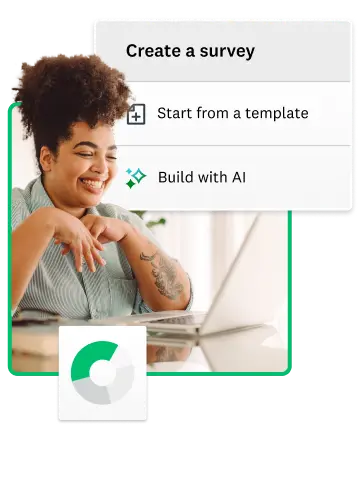
How to create a survey with SurveyMonkey in 7 steps
Power your business strategy with user insights. Learn how to create, launch, and analyze the results of a SurveyMonkey survey in minutes.
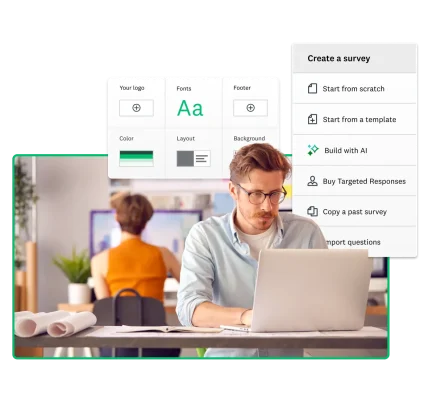
Eighty-four percent of full-time workers1 feel more confident in their decision-making when they have data to support their choices. Online surveys are a quick and efficient way to gather this information and validate business-critical decisions.
This guide will take you through the process of creating a survey, from defining your goals to analyzing the results. You will learn how to design, distribute, and analyze surveys by following best practices and expert tips. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped to create effective online surveys.
How to make an online survey in 7 steps

Creating an online survey with a clear plan is easy. Follow this simple 7-step framework we've developed over 25 years at SurveyMonkey.
Step 1: Identify the survey goals and objective
Start by defining clear, specific goals for your survey. Clear goals help focus your questions and ensure you gather relevant data. For example, are you aiming to improve customer service, measure employee satisfaction, or understand market trends?
Specific goals, like "identify top three employee concerns," provide direction. These goals guide your question design, helping you collect actionable insights. Knowing your objectives keeps your survey concise and targeted, making it more effective.
Step 2: Pinpoint your target audience
Know who you're surveying to tailor your questions. Understanding your target audience helps you use language and questions that resonate with them. Avoid jargon and use clear, simple language.
Consider demographic factors such as age, location, and interests. If you're surveying employees, use expressions familiar within your organization. If your audience is general consumers, keep the language straightforward and accessible.
Step 3: Determine the type of online survey
Choose the appropriate survey based on your goals. Different surveys serve different purposes; here are three standard online survey types.
Customer satisfaction surveys
Customer satisfaction surveys gauge customers' feelings about your products, services, and business practices. They provide insights into customer experiences, helping you understand what works and where to improve. These surveys are essential for keeping customers happy, loyal, and engaged with your brand.
Use customer satisfaction surveys to:
- Measure customer service effectiveness: Assess how well your team meets customer needs.
- Evaluate brand satisfaction: Understand overall customer happiness with your brand.
- Identify popular products or services: Find out what resonates most with your customers.
- Pinpoint areas for improvement: Discover specific aspects of your offerings that need enhancement.
- Gauge customer loyalty: Determine how likely customers are to stay with your brand.
Employee engagement surveys
Employee engagement surveys reveal how employees feel about workplace experiences. They help you understand the impact of your current systems and highlight areas needing improvement. Engaged employees are happier, more productive, and more likely to stay with your company.
Use employee engagement surveys to:
- Build an inclusive workplace: Gather insights on diversity and inclusion efforts.
- Understand employee sentiment: Measure satisfaction with salaries, benefits, and work conditions.
- Evaluate job satisfaction: Learn about overall job happiness and areas of concern.
- Assess manager effectiveness: Get feedback on leadership performance.
- Conduct exit interviews: Identify reasons for employee turnover and areas for improvement.
Market research surveys
Market research surveys help businesses understand their target market, informing better decision-making. These surveys are valuable for capturing consumer preferences, testing new ideas, and assessing market trends. They provide data that drives strategic planning and product development.
Use market research surveys to:
- Understand target audience opinions: Learn what your audience thinks about your brand, products, or services.
- Identify market gaps: Discover unmet needs and opportunities for growth.
- Test new products: Poll your audience and get feedback before launching.
- Evaluate ad campaigns: Measure the success of your marketing efforts.
- Assess brand awareness: Discover how well the market recognizes your brand.
- Benchmark against competitors: See where you stand compared to others in your industry.
Step 4: Write your survey
Your survey design is critical to the quality and usefulness of the data you collect. Craft straightforward, concise questions to gather the most accurate data. Well-designed questions can improve response rates and provide actionable insights.
Here's how to write effective survey questions:
Use formatting
Group similar questions to maintain a logical flow. Use page breaks, titles, and instructions to guide respondents. Proper formatting helps respondents understand the structure of the survey and reduces confusion. It also makes the survey easier to navigate, improving completion rates.
Be brief
Keep questions short and to the point to avoid overwhelming respondents. Brevity ensures that respondents remain engaged and are more likely to complete the survey. Long, complex questions can lead to frustration and dropout. Short questions are also easier to understand, leading to more accurate answers.
Stick to specifics
Focus on one idea per question to ensure clarity. Vague questions lead to ambiguous answers, which can complicate data analysis. Specific questions yield precise responses that are easier to interpret and act upon. This clarity helps you get the exact information you need without any guesswork.
Clarify answers
Provide clear options for answers and avoid language that respondents can interpret in multiple ways. Clear answer choices reduce respondent confusion and improve the data quality. By being explicit, you help respondents choose the most accurate option, leading to more reliable results.
Keep questions relevant
Use skip logic to ensure respondents only see questions that apply to them. These conditional controls keep the survey concise and relevant. Irrelevant questions can frustrate respondents and lead to survey abandonment. Relevant questions maintain respondent interest and improve the overall quality of the data.
Go easy on yes/no questions
Use yes/no surveys sparingly, as these questions don't capture nuanced opinions. Yes/no questions are straightforward but often lack depth. Use them for simple, binary information, but rely on more detailed question types to gather comprehensive insights. This approach provides a fuller picture of respondent opinions and experiences.
Know when to use matrix questions
Use matrix questions to gather detailed feedback efficiently, but don't overuse them, as they can overwhelm respondents. Matrix questions allow you to collect data on multiple items with consistent answer choices. These questions save time and effort for you and the respondent. But be careful, as too many matrix questions can lead to survey fatigue.
Rely on templates and question banks
Use survey templates and question banks to save time and ensure quality. Templates and question banks provide a solid survey foundation. They help you identify effective questions—including close- and open-ended questions—and streamline the survey creation process. Customizing these resources to fit your needs will result in a well-structured and insightful survey.
Step 5: Test the survey
Before launching your survey, conduct a pilot survey (externally or internally) to identify any design flaws.
A pilot survey, or test run, helps you evaluate instructions, layout, and questions. It's a small-scale test that saves you from costly mistakes later. A few dozen respondents are typically enough and don't have to be from your target audience. Focus on how they interpret the survey rather than their specific answers.
External surveys use respondents outside your primary study group, perfect for testing technical aspects. Internal surveys involve your target audience, providing realistic feedback on expected responses. After completing your pilot, refine your survey based on the feedback to ensure clarity and effectiveness. If necessary, run a second pilot to confirm improvements.
Step 6: Send your survey
Distribute your survey through multiple channels to reach a broader audience. Email is common, but consider using social media, website links, or direct messages. Ensure your survey is accessible on all devices, including mobile phones.
SurveyMonkey offers many ways to send your surveys:
- Web link: Create a URL or QR code linking to your survey to send or post it anywhere.
- Email invitation: Send customized email invitations to your contacts through SurveyMonkey. Track responses and send follow-up emails.
- Social media: Post your survey on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other social channels to reach a wider audience.
- Target audience: Buy responses through SurveyMonkey Audience if you don't have your list of survey takers.
- Website: Embed your survey or show a pop-up invitation on your website to capture responses from visitors.
- Manual data entry: Input responses collected offline or add responses for someone without an internet connection.
- Mobile SDK: Use a survey hash to add surveys to iOS or Android apps, ideal for app developers.
- Field survey: Collect responses using the SurveyMonkey Anywhere app—perfect for in-person collection points.
- Text Message: Text a survey link to your contacts. Recipients can tap the link to take your survey in their mobile browser.
Learn how to find survey respondents in 5 easy steps
Step 7: Send reminders and thank you emails
Boost response rates by sending reminders to those who haven't completed the survey. A gentle nudge 48-72 hours after the initial invite can significantly increase participation.
Limit reminders to avoid annoyance—no more than four. Always set a deadline for survey completion and stop reminders after this point.
Express appreciation to respondents with thank you emails to reinforce their valued input. With SurveyMonkey, you can automatically trigger thank you emails after the survey is completed.
What are online surveys?
Online surveys gather information from a targeted group via the internet. These digital surveys offer efficient and quick ways to gain insights and drive business decisions.
Online surveys are efficient, cost-effective, and flexible. They also provide immediate results and broad reach. This makes them ideal for modern data collection—whether for customer feedback, market research, or employee engagement.
Related: Why surveys?
Benefits of online surveys

Online surveys offer numerous advantages over traditional methods. They provide efficiency, cost savings, and immediate access to data, making them essential for modern data collection.
Increased response rate
Online surveys typically achieve higher response rates. Respondents can complete surveys on any device, making it convenient and increasing participation.
Lower, more affordable costs
Creating, distributing, and collecting online surveys is cost-effective. There's no need for large budgets or external agencies. You can manage everything on a single platform, making data accessible across your organization.
Real-time access
Online survey data is available immediately. You can analyze results and gain actionable insights without waiting for manual data entry. This reduces errors and speeds up decision-making.
Convenience
Online surveys are easy to create and distribute. With templates and sample questions, you can quickly design a survey that meets your needs. Respondents can access surveys on any device, anytime, increasing the likelihood of completion.
Additionally, online platforms simplify collection, analysis, filtering, and reporting. Automated tools provide instant insights, advanced filtering, and crosstab reports, making it easier to interpret data and share findings.
Design flexibility
Online survey platforms offer excellent design flexibility, allowing you to customize the layout and questions. Pre-made question banks provide ready-to-use answer choices, saving time while leveraging best practices from survey experts.
No interviewer
Respondents often feel more comfortable providing honest feedback online. The absence of an interviewer eliminates potential survey biases and encourages more candid responses.
Cost efficiency
Online surveys eliminate the need for printing, mailing, and manual data entry. Automated data collection and analysis save time and reduce costs, making surveys more affordable.
Accessibility
Your online surveys are accessible to everyone. Tools and checklists ensure your surveys are compliant with Section 508 and WCAG 2 standards. This inclusiveness increases your reach and response rates.
Challenges of online surveys
While online surveys have many benefits, they also come with challenges. Here are common problems and how to address them.
Inaccurate data
Online surveys can produce inaccurate data due to rushed responses or confusion. Ensure your questions are clear and specific to minimize confusion. Use logic features to skip irrelevant questions and keep respondents engaged. For example, if asking about product usage, provide options like "daily," "weekly," or "never" to capture precise data.
Limited sampling and respondent availability
Not everyone has internet access, which limits your survey reach, particularly for certain demographics or regions. To combat this, try combining online surveys with phone or face-to-face surveys to include these offline respondents. For example, in rural areas with low internet access, you may conduct phone interviews or attend community gatherings to collect more comprehensive data.
Possible email server issues
Emails can end up in spam folders, reducing response rates. Improve email delivery rates by using an identifiable sender name and subject line.
You may need to address technical issues when sending large email batches. Improve email delivery rates by setting up proper DNS records like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
SurveyMonkey works with your Internet Service Provider to automatically validate SPF, DKIM, or DMARC records. You don't have to worry about email servers and other technical matters.
Little oversight or moderator
Without a moderator, respondents may misinterpret questions or skip important sections. Pre-test your survey with a small group to identify unclear questions. Provide clear instructions and use validation rules to ensure respondents answer critical questions. For example, make critical fields required or use tooltips to explain complex questions.
By addressing these challenges and testing thoroughly, you can improve the reliability and effectiveness of your online surveys.
Frequently asked questions
- What are the main types of online surveys?
- How do I make an online survey?
- How do I make a survey with SurveyMonkey?
- How to analyze survey results?
Get additional resources from SurveyMonkey
SurveyMonkey has a vast library of resources for creating online surveys, including guides, case studies, videos, webinars, and more. You can also visit our Help Center for all product-related information to maximize your research success. Try our free survey platform to discover all of the features needed to create an online survey in minutes and collect real insights.
Now that you know how to create an online survey, start using SurveyMonkey today!
1This SurveyMonkey poll was conducted July 19-30, 2024 among a national sample of 5,876 U.S. full-time workers. Respondents for this survey were selected from the more than 2 million people who take surveys on our platform each day. The modeled error estimate for this survey is plus or minus 1 percentage point. Data were weighted for age, race, sex, education, and geography using the Census Bureau’s American Community Survey to reflect the demographic composition of the United States.
SurveyMonkey 101: Building your first survey
Join our free webinar and learn survey design fundamentals, AI-powered creation, and collaboration best practices.
Discover more resources

Solutions for your role
SurveyMonkey can help you do your job better. Discover how to make a bigger impact with winning strategies, products, experiences, and more.

Anonymous polls: What they are, benefits, and how to create them
Learn what anonymous polls are, why they matter, common use cases, and how to create them effectively for honest feedback.

Trend forecast: What's shaping brands, AI and workplaces
Learn the top 5 trends driving business in 2026

Travel survey questions: 40+ examples to improve guest and traveler feedback
Use these 40+ travel survey questions and templates to collect feedback, boost guest satisfaction, and improve every traveller’s experience.
Ready to get started?
NPS, Net Promoter & Net Promoter Score are registered trademarks of Satmetrix Systems, Inc., Bain & Company and Fred Reichheld.